Agile is a transformational mindset that has changed how organizations approach project management and product development. It is not basically a technique or a collection of rules. It is fundamentally a way of thinking that puts flexibility, teamwork, and continuous improvement ahead of defined procedures and copious paperwork. In this post, we’ll discuss Agile’s basic ideas, go over its guiding principles, and explain why it’s more of a philosophy than just a set of rules.
It is more than a method; it’s a way of thinking that puts flexibility, collaboration, and customer value first. it is frequently connected with software development. Agile places a greater emphasis on responding to change and making incremental progress than conventional, rigid techniques. However, It is a way of thinking that prioritizes flexible procedures and tools over people, communication, and customer satisfaction. It involves embracing change and using it to produce better results rather than mindlessly adhering to a set of predetermined rules. Agile teams operate in a setting that promotes exploration, education, and development. Let’s look at how Agile moves beyond the area of laws and regulations to become a way of life.
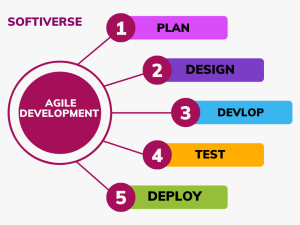
The fundamentals of agile
- People and Interactions Over Tools and Processes.
Agile prioritizes interactions with people. Tools and processes are important. Teams place a high priority on transparent communication and teamwork, dismantling silos and encouraging a sense of shared ownership.
- Following a plan while adapting to change.
Agile is aware that in a dynamic context, plans might become obsolete. it teams adapt to changes in needs, technology, and market situations rather than strictly following a plan. This versatility ensures that the final product stays in line with customer requirements.
- Iterative development
Agile projects are broken up into smaller iterations, each of which produces a useful component of the final product. With the help of this iterative methodology, teams may receive regular feedback and make adjustments based on practical knowledge.
- Client-centered Approach
Integrating customers throughout the development process is a key component of the agile methodology. By focusing on the needs and pain areas of the consumer, the final product will be more likely to succeed in the market.
- Multidisciplinary Teams
Teams are made up of people with a variety of talents, which promotes a collaborative environment. This diversity enables quicker problem-solving and an all-encompassing perspective of the project.
- Continuous Feedback Loops
Agile methodologies are deeply rooted in feedback loops. Teams can spot problems early and correct their course by routinely assessing and changing their work.
Agile Implementation in Various Industries
- Application Development
Agile’s founding industry was software development, where its guiding principles have excelled. Agile’s iterative methodology fits with the quick-moving tech industry.
- Marketing
Agile marketing helps teams to react quickly to customer and market shifts, ensuring that ads are still effective and relevant.
- Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing streamlines production procedures and enables businesses to swiftly adapt to changes in the supply chain and customer needs.
Advantages of Agile Philosophy
- Product Quality Improvement
Higher product quality is the result of iterative testing and ongoing feedback. Early bug detection results in higher customer satisfaction.
- Improved Client Satisfaction
Customers are more satisfied since the end product precisely meets their expectations when they are involved in the development process.
Agile is a concept that helps teams to accept change, communicate efficiently, and produce outstanding results; it is not a set of rigid rules. Agile supports organizations in thriving in a business environment that is rapidly changing by emphasizing people, agility, and consumer input.
 My Account
My Account 


